![By USSR Post [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://nootropicgeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/cosmonaut-stamps-1024x846.jpg)
Pronounced in English as: Droog poznayesta v bede.
Which means: A friend is known in trouble.
This saying, used as the English equivalent of “A friend in need is a friend indeed,” essentially sums up the Noopept supplement experience: At times of fair cognitive weather, Noopept shows up, but, meh, doesn’t do a whole lot. Noopept gets bored and takes it easy.
Yet, when sh** hits the fan, shredding the mind & cognition to pieces, that’s when Noopept steps up and becomes a true droog indeed… Or so I’m told. You can never have too many droogs, which is why I’m checking out Noopept in this review to see exactly how droogly this nootropic seems to be.
Page Contents
How Noopept Is Supposed to Work
N-phenylacetyl-L-prolylglycine ethyl ester (best known by the brand name Noopept–which I’ll be using to save you from eye strain) is often listed as a racetam compound for its structural & nootropic similarities to racetams, but it’s not really a true 2-oxo-pyrrolidine-based racetam.
It’s just… Noopept.
![That's not how you spell "Noopept"... By Themoreyouno [GFDL or CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://nootropicgeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Noopept_Box-300x225.jpg)
Okay, not really… By the time Noopept was trademarked by the Russians in 1996 as Ноопепт or GVS-111, the whole Cold War Arm’s Race thing was well over (or maybe that’s just what they want you think… Technically, Noopept was first synthesized in the 1970’s).
Unlike previous racetams, which sparked distrust & skepticism for their origins in Soviet Russia, Noopept was & has been viewed simply as a more potent, effective extension of the brain healthy nootropic racetam drugs.
Which is essentially what Noopept is sold as: A more potent racetam.
But don’t just take their word for it.
Let’s see what the research says:
Increases anabolic processes in hippocampus
Both single & chronic doses (up to 28 days) of Noopept has been noted to increase nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) RNA concentrations in the hippocampus (well, rat hippocampus). Theoretically, the increase in these factors has been associated with increased hippocampal formation & function, thereby increasing memory power. This is based on a previous association between neurotrophic factors and long-term memory.

Noopept in the Hippocamp
Additionally, in vitro hippocampal cell assessments have demonstrated an increase of inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) by Noopept, a bio-action in the hippocampus believed to induce an anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effect.
Induces sensitizing effect on cholinergic processes
More in vitro neuron samples with Noopept have demonstrated “cholinosensitizing” effects following the administration of Noopept, resulting in decreased cholinoreceptor antagonists and, consequently, increased receptor sensitive to neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which plays an important role in learning & memory.
Provides general neuroprotection on brain injury
Under conditions of oxidative stress & physical brain trauma, Noopept seems to deliver general neuroprotective benefits–perhaps either through antioxidant effect or cerebrovascular improvement. While these benefits have been observed in both animal & human subjects, Noopept has yet to demonstrate neuroprotection on otherwise healthy individuals.
Spikes neuronal excitation via NMDA & AMPA receptors
![By RicHard-59 (Own work, based on File:Activated NMDAR.PNG) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://nootropicgeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Activated_NMDAR.svg_-292x300.png)
By working with these glutamate receptors, Noopept may spike neuronal excitation, which perhaps explains the subtle psychostimulatory effects associated with the nootropic drug.
Noopept Benefits
Mental performance. Memory consolidation. Information processing. These are the benefits I quoted in my piracetam review, and I’m quoting them for Noopept as well, since it provides, more or less, the same racetam-like bio-benefits. All-in-all, Noopept’s benefits can be summed up as:
- Memory improvement. Short & long term.
- Mental stimulation. Subtle, yet apparent.
- Neuroprotection. Antioxidant detox & neuroregeneration.
- Neurocommunication. Quicker, efficient thinking.
Although Noopept isn’t a true racetam, it behaves very much like one.
Noopept vs. Piracetam
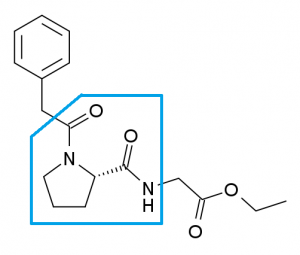
Much like piracetam, Noopept supports mental performance, memory consolidation, & information processing. Yet, unlike piracetam, Noopept is much more potent, the oft-cited figure describing it as 1000 times stronger than piracetam.
This is most likely drawn from the much lower required dosage of Noopept (10 – 30 mg daily) compared to piracetam’s (4800 mg daily), yet some researchers speculate that Noopept’s relative strength is much more variable–ranging anywhere from 200 to 50,000 times stronger than piracetam on a dose-to-dose basis.
This seems more realistic, considering that Noopept not only accomplishes similar benefits to piracetam at much lower concentrations, but seems to draw their effects out for much longer. I’d say this also illustrates the importance of not overdoing it on Noopept dosages, despite piracetam’s very high safety profile.
Researchers Have Suggested Noopept Might:
Improve conditions of mild cognitive disorder related to circulation & injury
In one of Noopept’s few human studies, 53 patients with mild cognitive disorder were administered either two daily doses of 10 mg Noopept or 1200 mg piracetam over 56 days. 41 subjects ended up finishing the trial, demonstrating improvements across-the-board for vascular-related injuries and some improvement for physical trauma patients. Measures that were improved included fatigue, anxiety, mood, motivation, irritability, and sleep, with Noopept showing more improvement than piracetam.
Enhance cognition under conditions of mild cognitive impairment
In a later open prospective study, Noopept’s effects were observed again under conditions of mild cognitive impairment. This time Noopept was administered for 12 months (1 year, in case you didn’t know) on 60 patients. Cognitive functions were measured before-&-after administration using neuropsychological tests, with significant improvement in cognition appearing around 2 months of Noopept (no changes for the control group). The results indicated that 2 months of 20 mg Noopept daily may significantly enhance cognitive function.
Prevent memory deficits (in rat models)
This study observes Noopept less as a “pro-memory” nootropic and more as an “anti-amnesic” compound. This harkens back to its role as a neuroprotector more so than as a neuro-enhancer. Even so, Noopept, studied on the three-way model of conditioned passive avoidance response, was shown to improve the spatial component of rat memory (i.e. memory of spatial arrangement, as in “where am I in this rat maze?”). Noopept was shown to accomplish this by decreasing cholinoreceptor antagonists, effectively enhancing acetylcholine expression.
How to Take Noopept
- 10 mg – 30 mg, once daily, up to 56 days is the safest known Noopept regimen.
- Capsule, tablet, & powder Noopept are available. Powder is the preferred option as it’s easier to monitor & alter intake than capsule & tablet forms.
- Inexperienced racetam users may start with piracetam before moving on to Noopept, considering it’s anywhere between 200 – 50,000 times stronger than piracetam on a dose-to-dose basis.
My Experience with Noopept
While Noopept remains unchecked on my nootropic “To-Do” list, I am familiar with the racetam class of nootropics. And judging by the research & reputation of Noopept, I’m anticipating the experience to be more or less (likely more) the same as piracetam–except more pronounced & more immediate.
Piracetam requires a “build-up” period of a couple weeks or so. Noopept reportedly does not.
This makes sense if the 1000 times stronger or 200 – 50,000 times stronger claims are to be believed.

With that in mind, I’d expect Noopept to have more of that “psychostimulation” that’s lacking in piracetam.
Having said that, I’d expect the Noopept experience to carry more or less (likely less) the same faults as the piracetam experience. The primary fault being:
- The inability to boost cognition under otherwise healthy cognitive function.
Is this really a fault?
Okay, not really. Saying it out loud does sound a little greedy. Especially considering that piracetam’s & Noopept’s abilities to sustain cognition is more than valuable as a benefit. Yet, the conditional nature of their benefits may come as a disappointment to users who viewed racetams as universal cognitive enhancers.
While I love racetams in theory, and I’m looking forward to see their therapeutic potential fully realized, I do think our perceptions on them are a little misguided. I think the reason they seem to work for only some is because their workings are only felt by some: Users with cognitive impairment.
Under sub-par conditions of cognition, racetams seem to work. Other initial levels of cognition, they still work, but they’re not quite felt.
Having said that, I’m confident that Noopept could be felt by more than piracetam. We’ll just have to wait for more research to see what all these feelings might mean.
Is Noopept a Good Nootropic?
Considering that Noopept stems from the original class of nootropics and manages to work like a stronger, more efficient piracetam, I’d say: Yes, Noopept is a good nootropic.
Unless you’re not a fan of racetams.
In which case, if the other racetams worked poorly for you, then I wouldn’t expect too much from Noopept. It’s essentially the same thing, but more.
Yet, that’s perhaps the best approach to Noopept: Start with lower-grade racetams (preferably piracetam as its the most similar to Noopept) to see how your body responds to them. If you like the experience, but want more… then, well, here you go: Noopept.
On the whole, racetams are mostly backed by high safety reviews. I don’t expect Noopept to stray too far from this. Yet, approach with caution all the same, considering it’s one of the least studied drugs on the list.
Overall Noopept Nootropic Power Rating
[yasr_multiset setid=0]
