I know, right? What a boring topic.
Asking whether or not glutamine is good for cognition is like discussing the health points of water. The long-&-short of it being: You just need it.
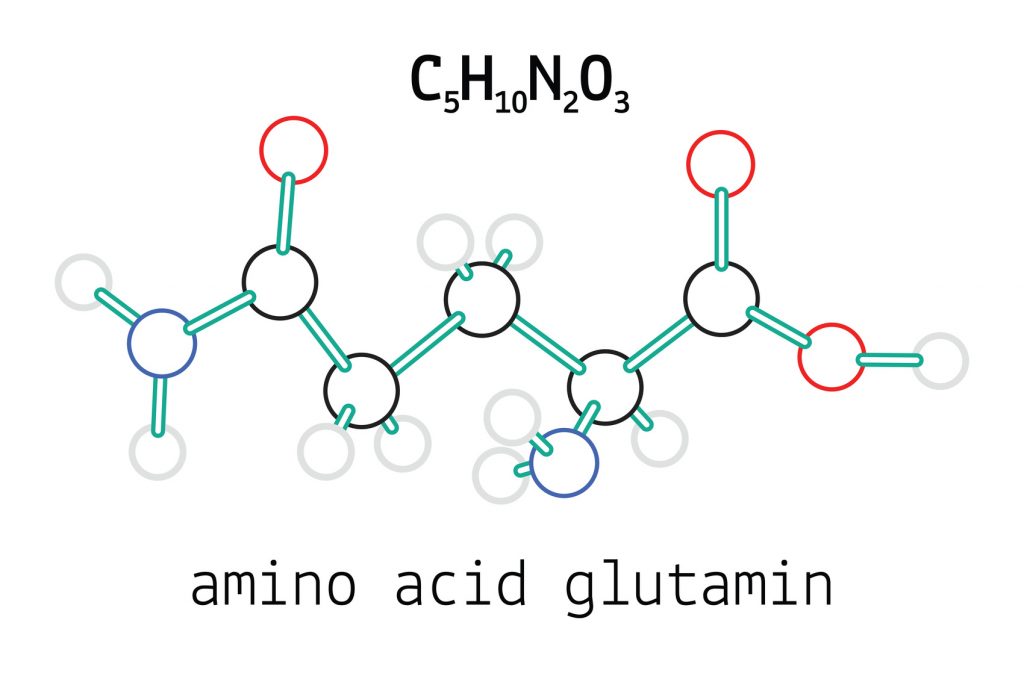
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the body, serving a variety of key roles–most notably protein synthesis. Yet, some nootropic users are exploring the nootropic potential of this conditionally-essential amino acid under the belief that its metabolic benefits may help to enhance cognition.
I will say that without glutamine cognition would be in grave danger.
But does that mean we need to supplement it?
Let’s read the review to find out.
Page Contents
How Glutamine Is Supposed to Work
You eat the glutamine, then suddenly your memory paints for you your entire history, dating back to the minute you were born (the minutes before you were born?), while you aggressively try to stay awake.
That’s how the glutamine works, right?
I’m basing this theory on the two brain chemicals bioactivated by glutamine:
- Glutamate – Involved in memory & learning processes
- GABA – Supports relaxation & sleep

Of course, glutamine doesn’t do any of this–otherwise we’d all have superhuman memory & relaxation powers, given that glutamine is found in various common dietary plants & proteins: e.g. meat & poultry, eggs, cheese, cabbage, beans, legumes, nuts.
Instead, glutamine seems to support & maintain general cognition, particularly as it relates to glutamate & GABA. Which is why some users have turned to supplementing the amino in addition to the diet, viewing it as a valid nootropic cognitive enhancer, based primarily on its role in:
The Glutamate/GABA-Glutamine Cycle
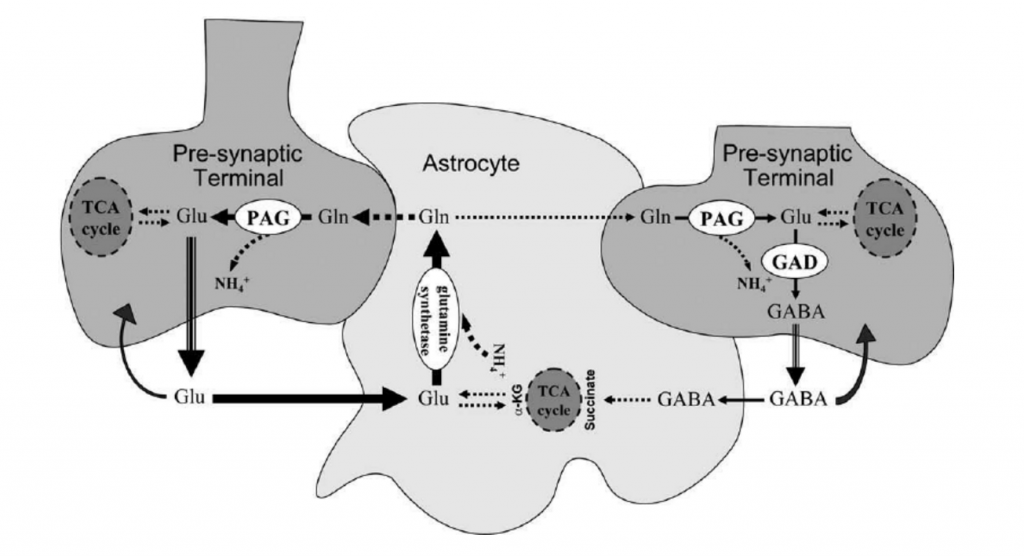
Glutamate & GABA are two neurotransmitter compounds essential to a number of basic cognitive functions. In fact, glutamate is the most abundant neurotransmitter in the body, believed to facilitate basic memory & learning processes.
And glutamine aids these chemicals through the glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle, a process that occurs between neurons & astrocytes–cells that release glutamine for neurons to uptake & utilize for the production of glutamate & GABA. When these neurotransmitters are released, astrocytes uptake them to keep the cycle going (as illustrated above).
Thus, when glutamine levels are down, the cycle derails, glutamate & GABA levels go down, and cognition & memory decrease.
Glutamine Benefits
But what about general cognition? Theoretically, glutamine supports memory & relaxation due to its supportive role of glutamate (memory) & GABA (relaxation). However, based on current research, glutamine only seems to maintain cognition, and may actually have negative health effects if consumed excessively. Given that glutamine is already adequately produced by the body, I’d venture that glutamine supplementation doesn’t have much of a nootropic benefit–but is worth consideration under conditions of heavy exercise and/or diminished brain states.
Researchers Have Suggested Glutamine Might:
Play a Key Role in Brain Glutamate Production
To confirm the role of glutamine in the glutamate-GABA-glutamine cycle this study employed a nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscope in observance of brain cell metabolism. In 8 volunteers the noninvasive approach identified 3 established pathways for neurotransmitter glutamate repletion, of which glutamine played an important role. The most notable finding: “Up to 30% of the glutamine transferred to the neurons by the cycle may derive from replacement of oxidized glutamate by anaplerosis.”—i.e. replenishment of cycle intermediates.
Support Recovery of Brain Injury (with Probiotics)
Energy & protein expenditure increases under conditions of brain injury, in effect increasing risk of secondary disease states & infection. The goal of this study was to evaluate the benefits of glutamine & probiotics administration on brain injury. Despite a questionable, weak design, the study observed a decrease in infection rate among the glutamine + probiotics group as compared to the control group, leading to the conclusion that “the enteral formula containing glutamine and probiotics decreased the infection rate and shortened the stay in the intensive care unit of brain injury patients.”
Maintain or Enhance Post-Exercise Cognitive Function & Reaction Time
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of L-Alanyl-L-Glutamine (AG) on cognitive function & reaction time following endurance exercise training: running on a treadmill at 70% of VO2max for 1 hour, then at 90% of VO2max until exhaustion. Endurance athletes underwent trials of no hydration, ingestion of only sports electrolyte drink, and a final two trials of sports drink plus either low-dose or high-dose AG. Results found improvements on cognition & reaction during the low-dose & high-dose AG trials, but no change with the electrolyte drink. The conclusion: “rehydrating with AG during submaximal exercise may maintain or enhance subsequent RT in upper and lower body activities compared to DHY. These same effects were not apparent when participants consumed ED.”
How to Take Glutamine
- No nootropic dosage has been officially established, ranging anywhere from 0.5 to 15 g in the research.
- Sports nutritional glutamine supplements supply 1 to 5 g daily dosages.
- Powder glutamine is the popular nootropic & sports nutrition form, but is also available in capsules (~500 mg per serving).
SIDE EFFECT: L-Glutamine & Neurotoxic Ammonia
The conversion of glutamate to glutamine helps clear neurotoxic ammonia, providing significant neuroprotection in the brain. However, glutamine also metabolizes to ammonia when consumed in high doses, leading researchers to view high-dose glutamine as the “Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity.” Twasn’t Odysseus but noxiously excessive glutamine that fell Troy!
My Experience with Glutamine
I do not consume glutamine for nootropic reasons, but I take it nearly daily–or whenever I workout, which (to be honest) is not daily. However, I don’t supplement glutamine as a standalone supplement, but rather in a mix of amino acids, proteins, etc. Particularly if I’m in the midst of a “bulking up” workout regimen.

Personally, I don’t consider glutamine as a nootropic, but rather as basic nutrition that affects cognition much in the same way that basic vitamins & minerals do.
When glutamine is off, cognition is off.
Yet, if glutamine is off, then a number of other health nutrients are likely off as well, which may negatively impact cognitive & physical functions. In such conditions, supplementing glutamine isn’t the answer. Correcting your diet is.
If I experience brain injury or concussion, I may up my glutamine intake. Otherwise I’ll only continue supplementing amounts that are conducive to building muscle.
Is Glutamine a Good Nootropic?
Nahh… Not really.
Labeling glutamine as a “nootropic” is a stretch in itself, based on the presupposition that all nootropics are intended to enhance cognition and not simply maintain it.
Glutamine is great for maintaining cognition.
Particularly for weight trainers & athletes.
For everyone else, glutamine is just basic nutrition. It’s important nutrition, far from being a negligible supplement, but not a compound you should actively seek out to boost your brainpower. There are other, better supplements for that.
Overall Glutamine Nootropic Power Rating
[yasr_multiset setid=0]